Knee joint pain can be an insidious and debilitating condition that affects people of all ages. Whether you’re an athlete, a fitness enthusiast, or simply someone going about their daily routine, understanding the causes of knee joint pain is essential for preventing and managing this discomfort. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the various factors that contribute to knee joint pain, shedding light on the underlying causes and potential solutions.
Causes of Knee Joint Pain
Osteoarthritis: The Wear and Tear Factor
Osteoarthritis is one of the leading causes of knee joint pain, especially among older individuals. This degenerative condition occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones in the knee joint wears down over time. As a result, bones can start to rub against each other, causing pain, inflammation, and stiffness.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Autoimmune Culprit
In contrast to osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis represents an autoimmune condition in which the body’s immune system erroneously targets the synovium, which constitutes the protective lining encompassing the joint membranes. This autoimmune response triggers inflammation, one of the significant causes of knee joint pain. Inflammation caused by rheumatoid arthritis can lead to knee joint pain and even deformities if left untreated.
Overuse and Injury: Straining the Knee
Engaging in repetitive activities or high-impact sports can strain the knee joint, leading to pain. Ligament tears (like the ACL or MCL) and meniscus injuries are common sports-related causes of knee joint pain. Such injuries often require medical attention and, in some cases, surgery.
Obesity: The Weighty Connection
Carrying excess body weight places significant stress on the knee joints, making it one of the prominent causes of knee joint pain. This added pressure can contribute to the breakdown of cartilage and the development of osteoarthritis. Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for preventing knee joint pain and promoting overall joint health.
Muscle Weakness and Imbalances
Imbalances in muscle strength around the knee joint can be significant causes of knee joint pain. These imbalances can lead to poor alignment and tracking issues, putting undue strain on the joint and causing discomfort. Strengthening the muscles around the knee through targeted exercises can play a crucial role in preventing such imbalances and the resulting pain.
Age and Genetics: Uncontrollable Factors
Age plays a significant role in the development of knee joint pain, as wear and tear naturally accumulate over time. Additionally, genetics can play a crucial role in influencing one’s susceptibility to certain joint conditions. Understanding these uncontrollable factors can help individuals take proactive steps to manage knee health and mitigate potential causes of knee joint pain.
Lifestyle and Posture: Everyday Impact
Prolonged periods of sitting, improper posture, and poor biomechanics can significantly contribute to knee pain. Being mindful of ergonomics and actively maintaining good posture can play a crucial role in alleviating unnecessary strain on the knee joints, thereby addressing one of the common causes of knee joint pain.
Other Medical Conditions: Secondary Effects
Certain medical conditions such as gout, lupus, and infections can also lead to knee joint pain. It’s important to address these underlying conditions to effectively manage knee pain.
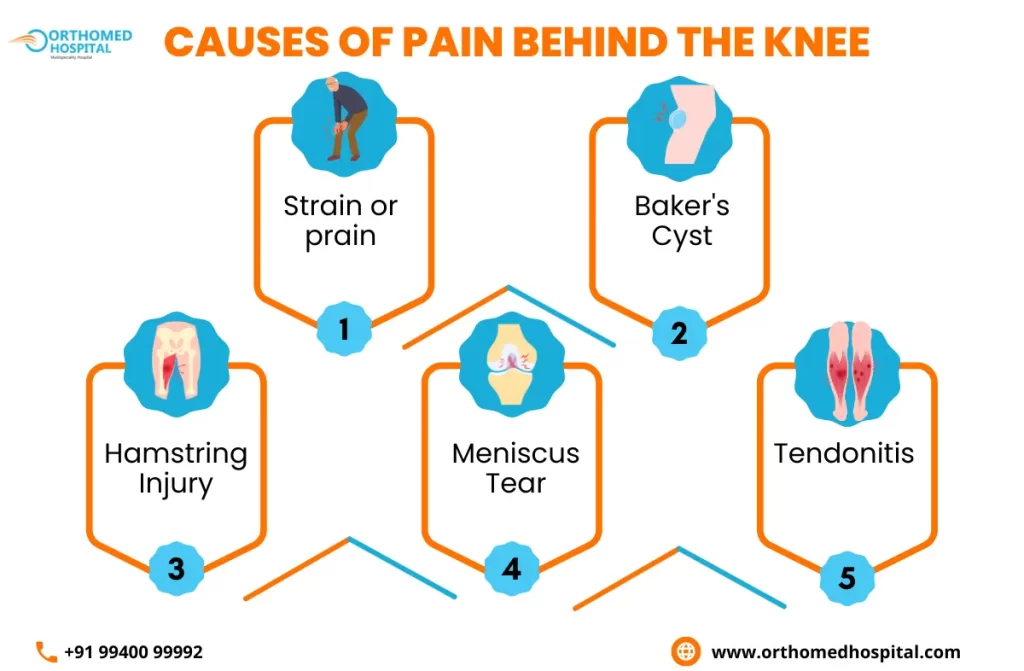
Causes of Pain Behind the Knee
Pain behind the knee can have various causes, ranging from minor issues to more serious underlying conditions. Here are some common causes of pain behind the knee:
- Strain or Sprain: Overuse, sudden movement, or excessive strain on the muscles, tendons, or ligaments behind the knee can lead to pain. This could be due to activities like running, jumping, or sudden stops and starts.
- Baker’s Cyst: Also known as a popliteal cyst, this is a fluid-filled sac that forms behind the knee. It can cause pain and stiffness, often resulting from underlying conditions like arthritis or meniscus tears.
- Hamstring Injury: The hamstring muscles run along the back of the thigh and attach behind the knee. An injury or strain to these muscles can lead to pain in the back of the knee.
- Meniscus Tear: The menisci are cartilage pads in the knee joint that can tear due to sudden twisting or excessive force. This can result in pain behind the knee, especially when bending or straightening the leg.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendons behind the knee, such as the popliteal tendon, can cause pain. This is often due to overuse or repetitive activities.
Conclusion
Knee joint pain is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors. By understanding the various causes, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent knee pain and maintain optimal joint health. Lifestyle modifications, regular exercise, weight management, and seeking medical advice when needed are all important strategies for keeping knee pain at bay. Remember, early intervention and a holistic approach to joint health can lead to improved quality of life and reduced discomfort in the long run.
Read also Food for Healthy Bones.